Three-parent embryos: Medical world falls out over eggs, cells and terminology
Professor claims terms are misnomers designed to make it easier for the public to accept the process
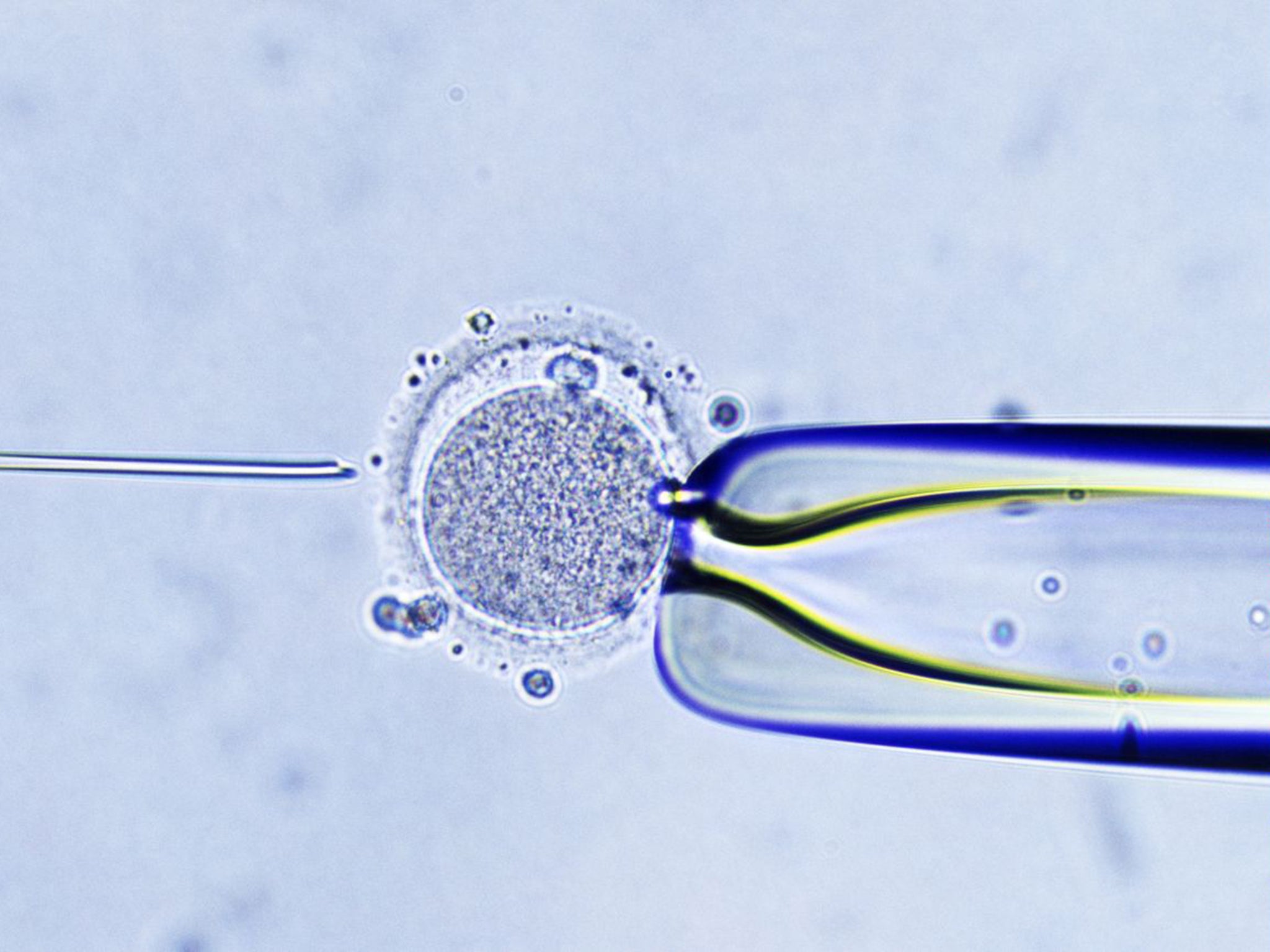
It may seem strange that an expert in cloning – the man who produced the first clones of an adult monkey – is now dabbling in a technique that has become widely known as “mitochondrial donation”, a term with the more vulgar moniker of “three-parent” embryos.
Shoukhrat Mitalipov has earned a global reputation as a superb experimentalist able to perform procedures on eggs and embryos that have defied many of his peers. Born in the Soviet Union, in what is now Kazakhstan, and trained in Moscow, Dr Mitalipov, 53, emigrated to the United States in the mid-1990s. Since then he has created shock-waves around the world with his prowess in the manipulation of eggs and embryos.
He now intends to use mitochondrial donation as a treatment for age-related infertility, providing he receives approval for clinical trials.
For many this is confusing, and the reason has much to do with how the scientific terminology surrounding this technique has been subtly manipulated over recent years to make it more publicly acceptable.
Mitochondrial donation is also known as mitochondrial transfer, and at its simplest description it involves the merging of three people’s DNA into a single embryo. However, the technique is actually more subtle than suggested by the terms “mitochondrial transfer” and “mitochondrial donation”.
Mitochondrial Donation - how it works
Show all 1Stuart Newman, professor of cell biology at New York Medical College, said these terms are misnomers designed to make it easier for the public to accept the process.
“No transfer of mitochondria (the organelles that extract energy from fuel molecules and make it available for the cell’s function) is involved in these ‘three-parent’ procedures,” Professor Newman said.
He points out that the two techniques for producing “three-parent” embryos do not involve the transfer of mitochondria but result in the transfer of a cell nucleus from one woman’s egg (the “patient”) to the egg of another woman (confusingly called the “donor”), which has had its own nucleus removed.
When Britain’s Department of Health first talked about the possibility of using mitochondrial transfer in this way, in a report in 2000, it called the technique “oocyte [egg] nucleus transfer”, because of its similarity to “cell nucleus transfer”, the cloning technique used to create Dolly, the first sheep to be cloned from an adult cell.
Egg nucleus transfer is not cloning, because it involves the fertilisation of egg by sperm, but it is broadly the same process. This is why Dr Mitalipov – a cloning expert – is now involved in mitochondrial donation, a term now widely used by the Department of Health and the Wellcome Trust, the multibillion-pound research charity that funds the Newcastle team. This change in terminology may sound more benign than “egg nucleus transfer” and is closer to organ donation, with which it is wrongly compared.
Professor Newman is not impressed: “A kind of omertà among scientists and bioethicists has prevented a significant number of them from representing to the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority and the [US] Food and Drug Administration, and the press, the gravity of these alterations. But the health implications and the eugenic outcomes these procedures would enable are too great to ignore,” he said.
Subscribe to Independent Premium to bookmark this article
Want to bookmark your favourite articles and stories to read or reference later? Start your Independent Premium subscription today.

Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies