Review: A female genius ... By James Essinger
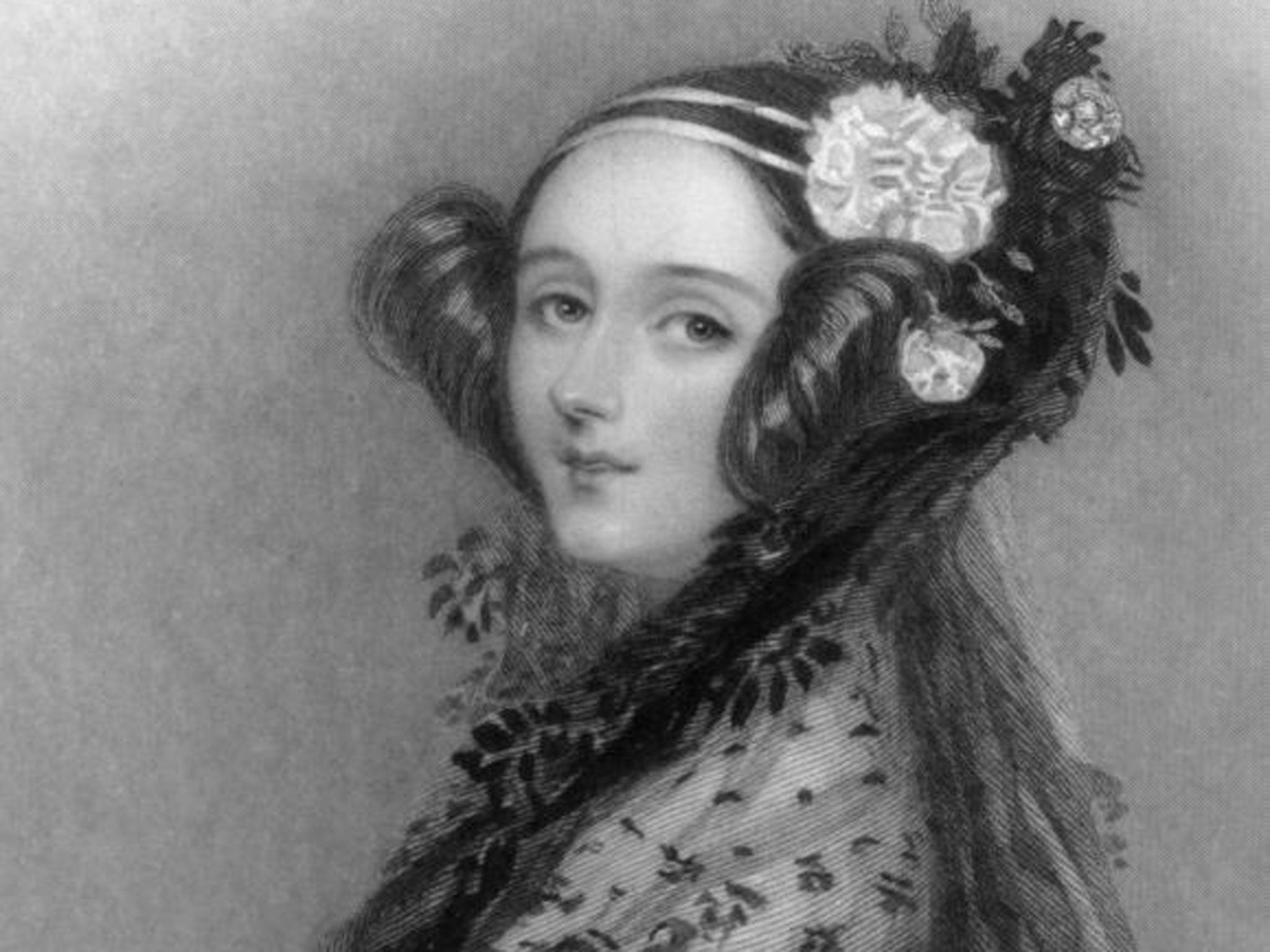
The history of science is punctuated by eureka moments of great discovery, but it’s also full of less well-known “what might have beens”. One such agonising narrative is the story of Charles Babbage’s Analytical Machine which, had it received the financial backing and development it needed, might have kick-started the computer age a century sooner.
Another is how Ada Lovelace might have become a household name. Ada was the daughter of Annabella Millbanke and Lord Byron, the poet’s only legitimate child. He never knew her; his wife fled in the night when his daughter was weeks old, after a short and often brutal marriage. Her friends enlightened the world about Byron’s incestuous relations with his half-sister, Augusta, which forced him into exile. In Essinger’s accessible biography, Annabella emerges as a controlling, highly intellectual mother with long-lasting influence over her more imaginative and emotional daughter.
But Ada had a mind of her own, although as fascinated by mathematics as her mother (Byron unkindly referred to Annabella as the “princess of parallelograms”). From early on she conjured up plans for a flying machine, and as a young woman she even eloped (mother soon called her back and preserved her reputation). Soon, she was suitably married off to William Lovelace, and her relationships with the mathematician Mary Somerville and the inventor Babbage really impacted on her. Babbage had completed a calculating machine, the Difference Machine, but it was his next, the unfinished Analytical Machine, that captivated Ada.
It was Ada who saw the machine’s real potential. Their surviving correspondence comprises 85 letters from Ada and 25 from Babbage, although Essinger is confident that Annabella destroyed many of Babbage’s letters after Ada’s death. Annabella seems even to have suspected the widower Babbage of considering Ada as a possible wife before her marriage, a demonstration of how close they had become.
In 1843, Ada published her translation of an Italian inventor’s article about the Analytical Machine, but she went further, advising Babbage on how to develop it beyond mathematics – she made “a wonderful and enormous conceptual leap” linking the machine to our understanding of the natural world and advocating “a new, a vast and a powerful language” to be “developed for the future use of analysis.”
The “digitisation of daily life” was envisioned by Ada, nobody else. Her early death from cancer, and Babbage’s possibly misogynistic refusal to accept help from a largely self-educated woman, will forever have us wondering what might have been.
Subscribe to Independent Premium to bookmark this article
Want to bookmark your favourite articles and stories to read or reference later? Start your Independent Premium subscription today.

Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies