Human nervous system actively works to preserve energy during exercise, scientists say
New study indicates humans may be genetically lazy

The human body's nervous system actively works against you when you exercise, according to new research.
Canadian researchers attached leg braces to nine volunteers to change their gait and found within minutes each participant modified their walking pattern to conserve energy.
But, the changes made only saved each individuals body a tiny amount of energy – the calorie equivalent of “peanuts” according to one researcher.
The human body carefully recalibrates its movements to conserve energy, neatly fitting into a tendency to put as little effort into tasks as possible or that humans are genetically lazy, the scientists from Vancover’s Simon Fraser University claim.
“Here we have provided a physiological basis for this laziness,” researcher Max Donelan claimed in the study published in journal Current Biology.
In the research, the Canadian scientist wrote “the nervous system subconsciously monitors energy use and continuously re-optimises movement patterns in a constant quest to move as cheaply as possible.
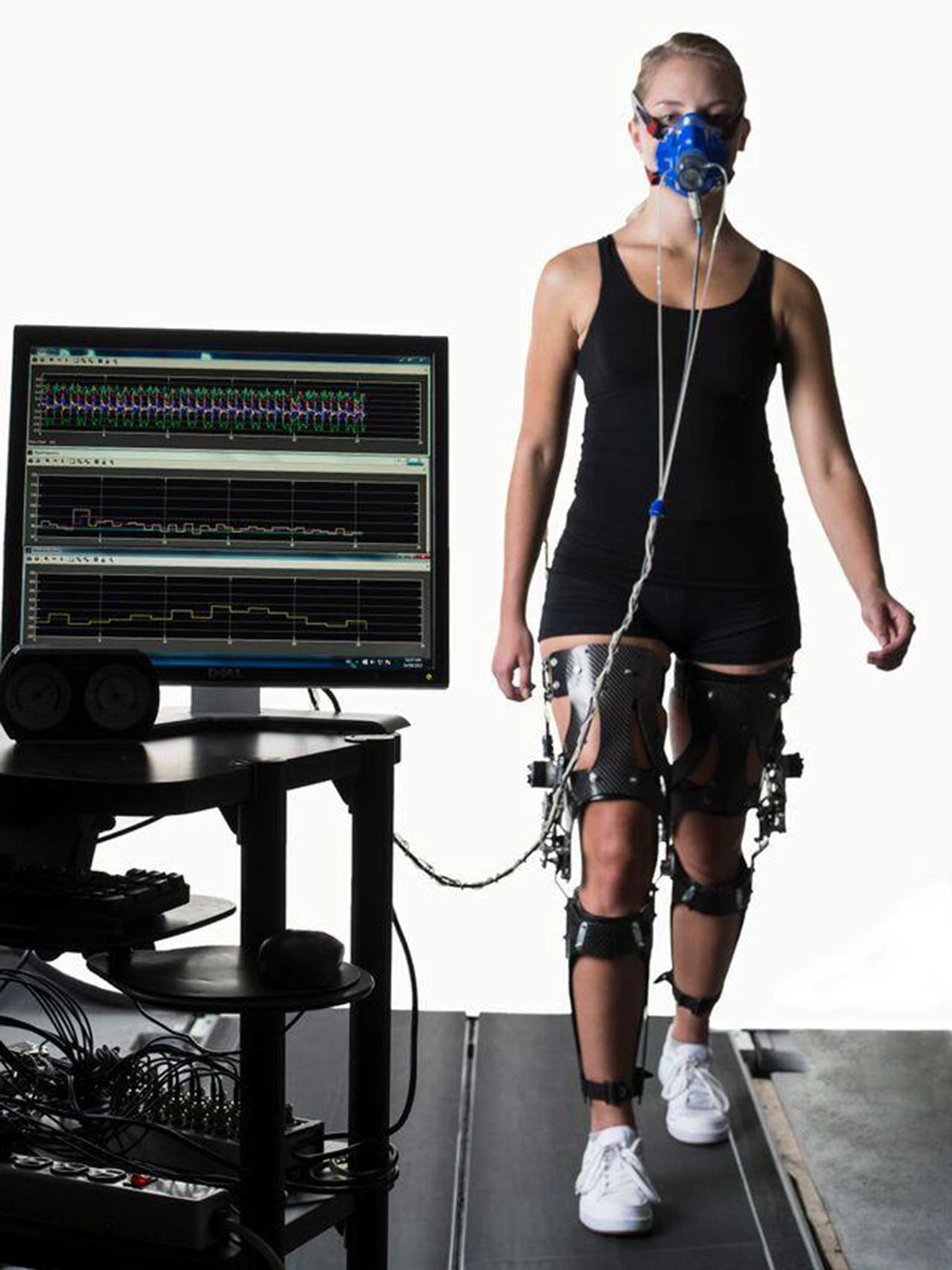
“We think that minimising energetic cost is a principle that guides most of our movements.”
The research could mean even while exercising, the body is trying to work out how to expend the least energy possible – somewhat nullifying the point of exercise.
However, scientists were careful to say that more research was needed. It is unknown how the body’s thousands of muscle-nerve components knit together to conserve energy.
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments