Just how credible is the Treasury's Brexit forecast? The answer in two charts
Other forecasters have projected a considerably smaller negative economic impact from Britain leaving the European Union.

A new analysis by the Treasury asserts that "Brexit" would leave UK GDP 6 per cent lower by 2030, costing every household in the country £4,300.
It’s important to understand what this means and what it doesn’t mean. It doesn’t mean the economy will be 6 per cent smaller than it is today if we leave the European Union.
It means GDP will be 6 per cent smaller than it would otherwise be if the economy carried on growing at the expected rate of around 2 per cent a year over the next 15 years. The 6 per cent projected loss in 2030 is relative to a counterfactual path of economic growth:
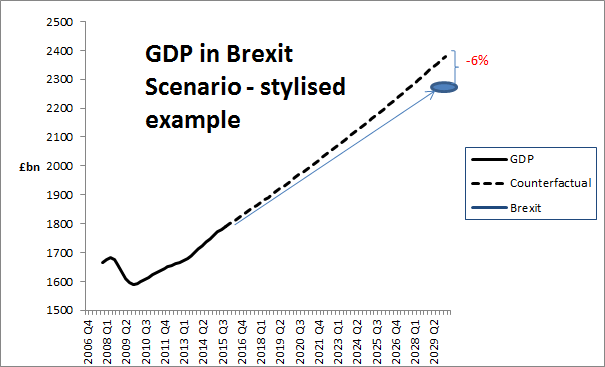
And how does the Treasury get the £4,300 per household figure? Well they divide the 6% shortfall (calculated as a cash figure in today's money) by 26 million, which is the number of households in the UK. So again it doesn't mean that families will be £4,300 worse off than they are today. But worse off relative to the counterfactual growth in their incomes over the next 15 years.
So how does the Treasury’s figure compare with those of other forecasters?

The answer is significantly worse:
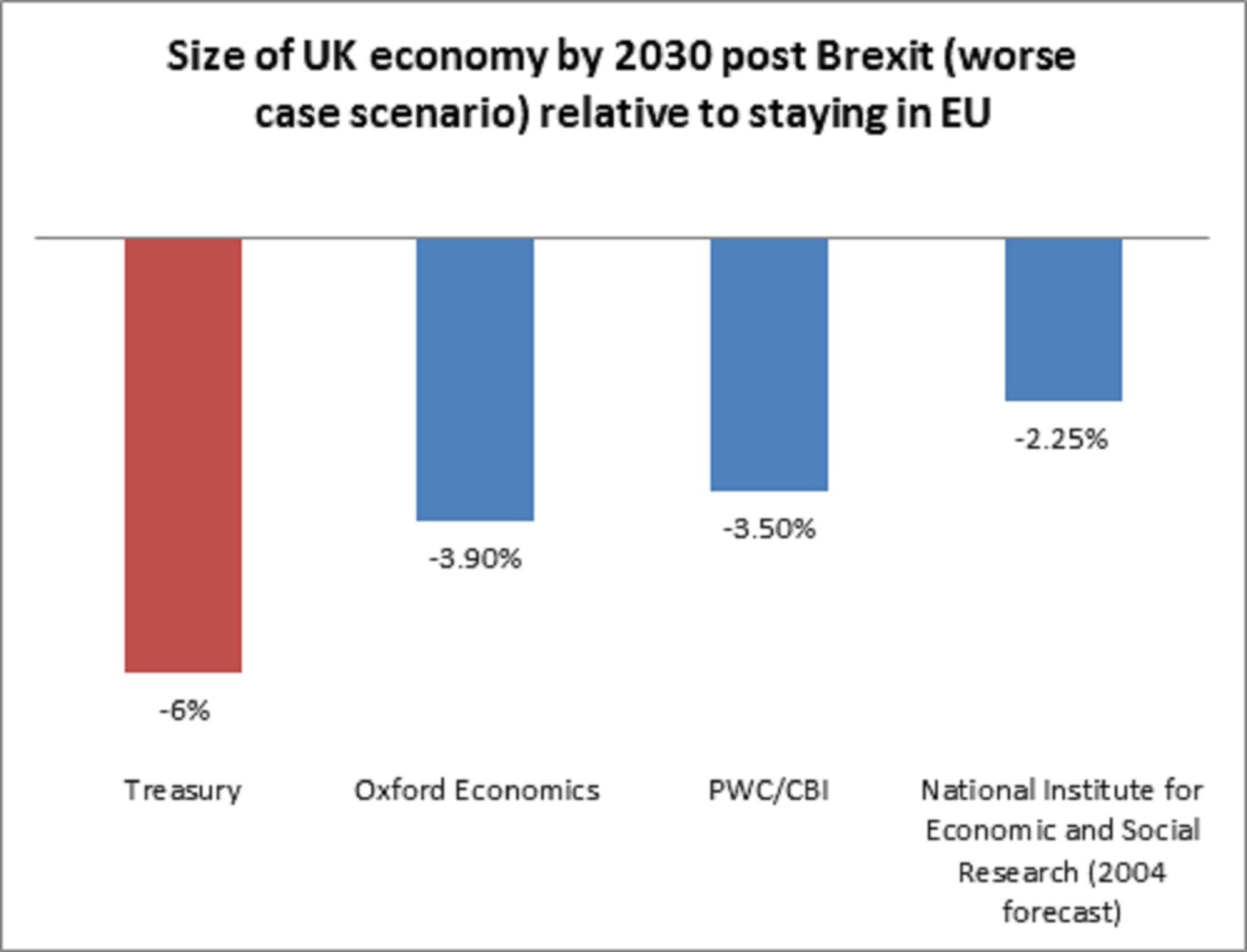
The economic consultancy Oxford Economics and the accountancy firm PwC have recently presented much less severe damage. And the think tank/forecaster NIESR in 2004 produced some work also suggesting a much less painful long-term shock.
So how can there be such variation in predictions?
The answer is that forecasts depend on economic models. And economic models depend on the inputs. If you put in a pessimistic input, for instance if you assume that the UK will not be able to negotiate a decent trade agreement with the EU post-Brexit, you will get a bigger shock to the economy. If you assume a decent trade agreement in your model the impact is much less painful.
The key in the coming hours will be to pore over the Treasury’s assumptions and inputs. If they are unrealistically negative the credibility of this document will be undermined.
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments
Bookmark popover
Removed from bookmarks