Ebola: Virus may have become more contagious after mutating since start of outbreak, scientists warn
World Health Organisation warns that in Guinea, only 30 per cent of new cases are known contacts of Ebola patients
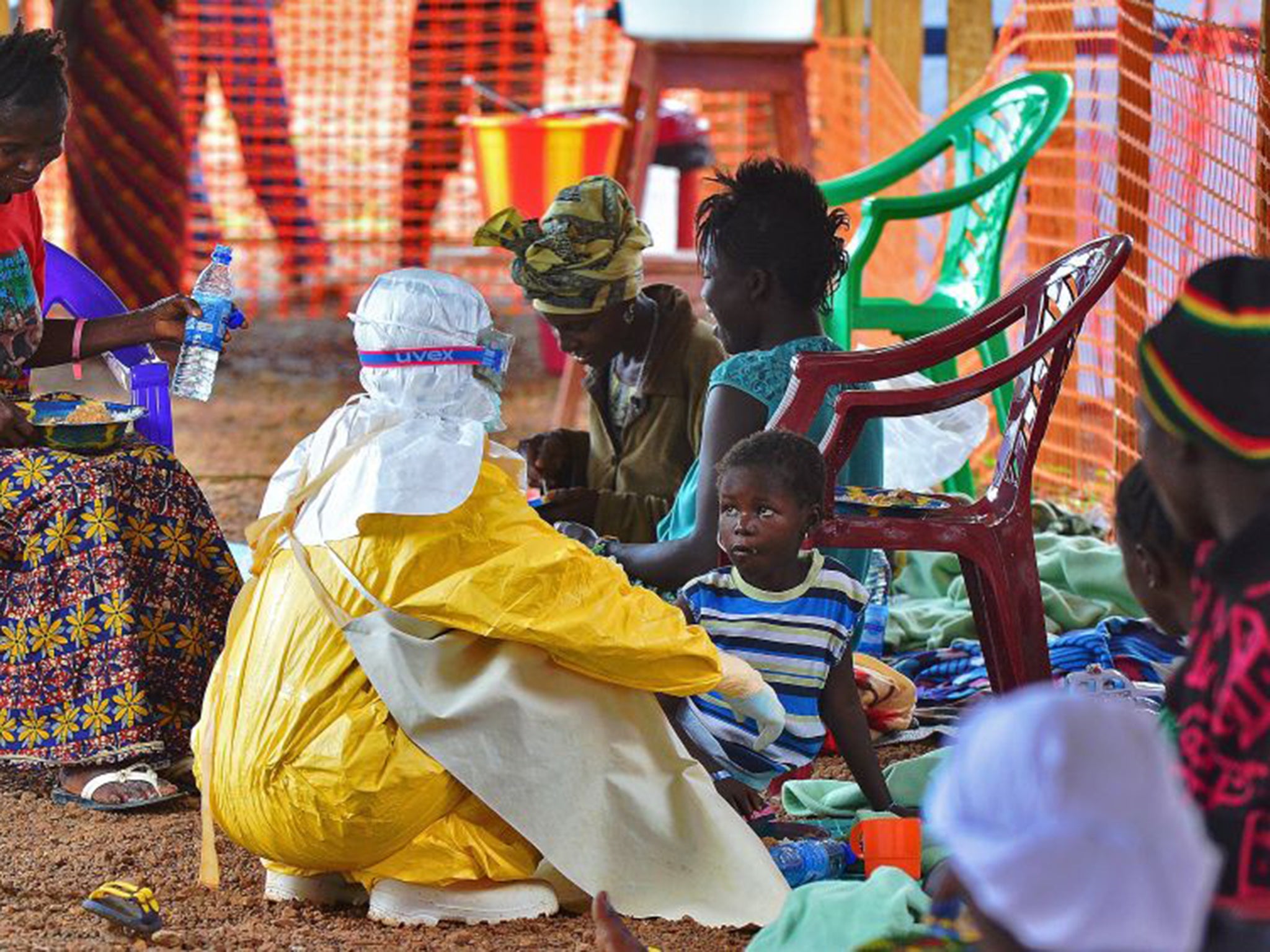
The Ebola virus may have become more contagious after mutating since the start of the current outbreak, scientists have warned.
Researchers at the Institut Pasteur, in Paris, where investigations are underway into whether the virus has become more contagious, have said there have been several cases where no symptoms were seen.
The research comes as the World Health Organisation warned that in Guinea, only 30 per cent of new cases are known contacts of Ebola patients – meaning officials have no idea how the majority of patients are becoming infected.
Dr Anavaj Sakuntabhai, human geneticist at the Institut Pasteur, told BBC Radio 4's Today programme: "We know that it has changed and it's changed quite a lot, and that is very important for diagnosis and for treatment."
He said it was important to know how the virus had changed in order to keep up with "our enemy".
Dr Sakuntabhai said there had been several cases reported where no symptoms had been seen in patients.
He said: "There's more report of that and these people may be the ones who can spread the virus better, we still don't know that yet. The virus can change itself from more deadly into less deadly but more contagious and that is something that we are afraid of."
Despite fears of a mutation of the virus, the WHO has said health officials are now focused on ending the current outbreak, rather than just slowing the spread of the virus.
The UN health agency said Guinea, Sierra Leone and Liberia – the three most affected countries – have reported fewer than 100 cases in the past week for the first time since June.
The current epidemic is the biggest ever outbreak of Ebola, and is believed to have killed more than 8,000 people since it started in March.
Bruce Aylward, who is leading the WHO Ebola response, said the virus is not under control, despite the progress made, and warned outbreaks often come in waves.
"This is like being in bed with two cobras, and one of them is dead," he said.
"You still have an incredibly dangerous situation."
Jerome Oberreit, secretary general of Doctors Without Borders, said: "We cannot say the epidemic is under control."
Mr Oberreit told a WHO Ebola meeting on Sunday that there was virtually no sharing of information about the risks of Ebola cases crossing the borders among the the three countries in west Africa.
He said surveillance teams lacked basic resources in order to track down Ebola patients and blamed the inability to contain the outbreak on "international negligence."
Additional reporting by PA
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments