CO2 levels expected to rise rapidly in 2019, Met Office scientists warn
'Worrying' results as greenhouse gas reaches record levels due to burning fossil fuels and dry landscapes unable to suck it up

This year will see one of the biggest CO2 surges in more than six decades of measurements, according to the Met Office.
Rising emissions due to the world’s continued appetite for fossil fuels will combine with reduced absorption of greenhouse gas by withering grasslands and forests.
Describing the prediction as “worrying and compelling”, scientists said it was an urgent reminder that the time to cut out carbon is now.
CO2 levels will be at a record high once again after emissions reached unprecedented levels last year, dashing hopes the world had finally hit “peak carbon”.
Besides fossil fuels pumping out the harmful gas, natural weather fluctuations will exacerbate the problem as they hamper the ability of carbon sinks to store it.
In 2019 an upward swing in tropical Pacific Ocean temperature will make many regions warmer and drier.
As drought sets in and plants dry out, they will be less capable of sucking CO2 from the atmosphere, and massive deforestation in places like the Amazon is making this problem even worse.
The new predictions were based on monitoring at the Mauna Loa observatory in Hawaii, which has registered a 30 per cent increase in the concentration of CO2 since 1958.
“Carbon sinks have saved us from what has already happened – the future rise would have been about double if it wasn’t for the sinks. So we are lucky they exist, to be honest,” Professor Richard Betts of the Met Office Hadley Centre told The Independent.
“But the sinks themselves are affected by the climate, and that’s an important thing because it shows that as climate change continues in the future it may affect their strength.”
If emissions continue to rise, a major concern is that the carbon sinks currently storing carbon will cease to function, potentially leading to uncontrollable warming and a scenario dubbed “hothouse Earth”.
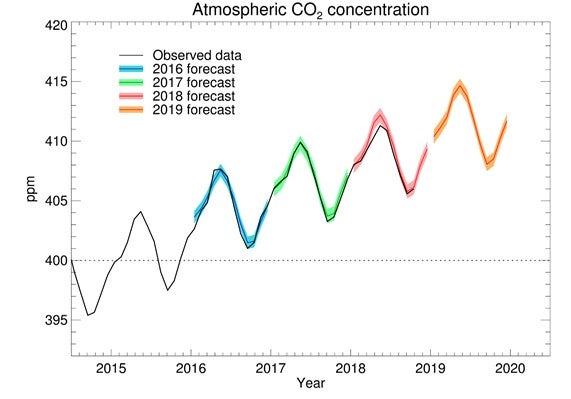
Last year Mauna Loa observatory recorded concentrations of over 410ppm in April, marking the highest level that had been reached in at least 800,000 years.
This year CO2 levels in the atmosphere are likely to hit 411 parts per million (ppm).
The Met Office forecast predicts the average increase in CO2 will be around 2.75ppm, the third largest annual rise on record, matched only by two years in which El Nino Pacific warming events took place.

CO2 is by far the biggest contributor to climate change, and global efforts to prevent environmental disaster largely focus on transitioning away from industries that pump it into the air.
Scientists welcomed the new data collected in Hawaii, describing it as “a call to innovate with rapid and radical responses” to the looming crisis.
“We need to reduce emissions from fossil fuel use, increase soil carbon sequestration to ‘lock-up’ CO2, decelerate deforestation and land conversion, and promote less polluting more sustainable agriculture,” said Professor Nick Ostle from Lancaster University, who was not involved in the Met Office research.
“It’s a massive challenge but there are real opportunities to make an impact individually and globally.”
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments
Bookmark popover
Removed from bookmarks