Nasa rover to make oxygen on Mars
Plan paves the way for future manned missions
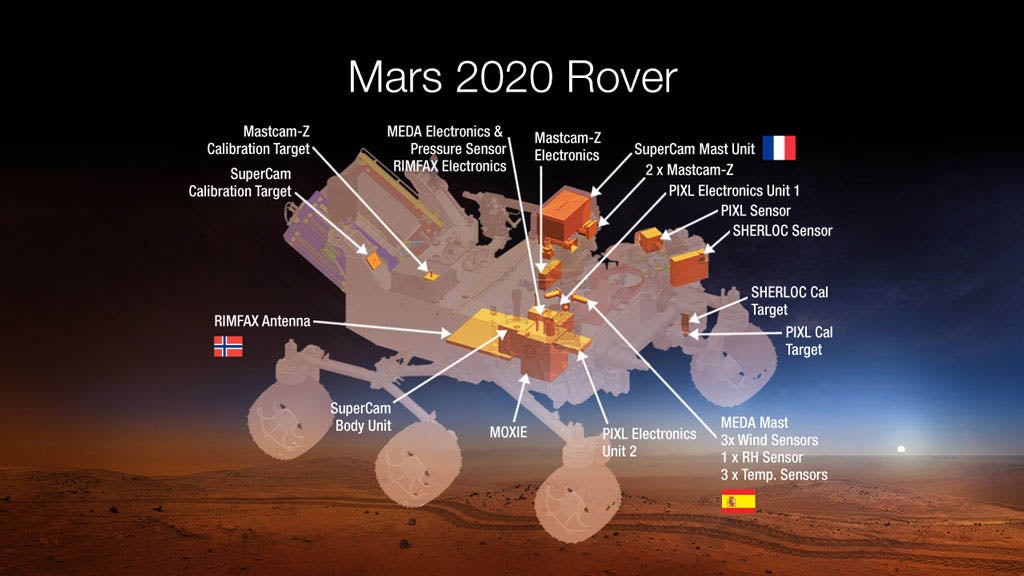
Just one month after NASA’s Curiosity rover completed an entire martian year on the surface of Mars, the world’s premier space organisation announced ambitious plans to prepare the planet for man’s arrival.
Just one month after NASA’s Curiosity rover completed an entire martian year on the surface of Mars, the world’s premier space organisation announced ambitious plans to prepare the planet for man’s arrival.
The Mars 2020 rover, due to land in 2021, and equipped with special instruments designed to convert the planet’s carbon dioxide atmosphere to oxygen, is the most advanced project in the organisation’s Mars Exploration Program.
Where Curiosity is still investigating the planet’s climate and geology, and the 2016 InSight lander will look into the deep interior of Mars, the 2020 mission will test NASA’s abilities to harvest the alien atmosphere and repurpose it to support life.
“Today we take another important step on our journey to Mars,” said NASA Administrator Charles Bolden.
“While getting to and landing on Mars is hard, Curiosity was an iconic example of how our robotic scientific explorers are paving the way for humans to pioneer Mars and beyond. Mars exploration will be this generation’s legacy, and the Mars 2020 rover will be another critical step on humans’ journey to the Red Planet.”
The key device designed for the $1.9 billion project is called MOXIE, and it works like engine but in reverse, according to Michael Hecht, the MIT scientist running the tests. It will make three-quarters of an ounce of oxygen an hour.
Should this work, then a device 100 times that size would be launched to Mars two years before astronauts are sent sometime in the 2030s.
The other key concept on the 2020 mission is the creation to rocket fuel from either light hydrogen brought from Earth or chemicals found on Mars’ surface or in its atmosphere.
This exciting announcement comes days after NASA announced Opportunity, the rover launched in 2003, had travelled more than 25 miles, breaking the record for off-Earth distance travelled.
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments
Bookmark popover
Removed from bookmarks