Where you live determines what age you die, US study claims
New data shows that differences in life span among low earners are more dependent on local policies, exercise and smoking than access to health care

For low-income Americans, where they live has a large bearing on the age at which they die.
A new study has placed a strong link between the income gap between rich and poor and where that person lives in the United States.
While the richest people in the US are living around three years longer in the new millennium, the poorest people are not living any longer than before.
Data from the Journal of the American Medical Association’s Health Inequality Project shows that the average life span is also strongly dependent on local policies which aim to improve behavioural habits like exercise and smoking.
“You want to think about this problem at a more local level than you might have before,” Raj Chetty, a Stanford economist who is the study’s lead author, told The New York Times.
The report places little emphasis between a region’s spending on health care or how many people have health insurance as a measure for how long someone will live. Neither does the report claim that unemployment plays a large factor. Simply put, rich people are less likely to smoke, be obese or suffer from stress.
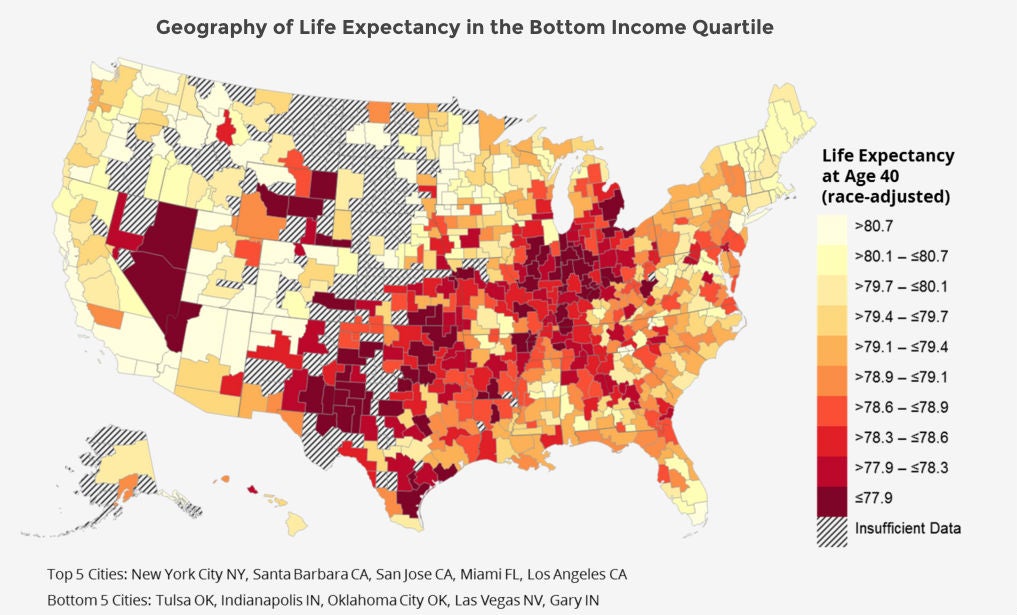
Looking locally, the largest differences in life span of low earners takes place in individual cities. While low-income people live six years longer in New York than in Detroit, the difference is only one year for high-earning Americans.
One of the sharpest differences is in Tampa, Florida and Birmingham, Alabama, where low-income people have lost 2.2 years and gained 3.7 years during the 2000s respectively.
The research, which took three years to compile, argued that the poor are living longer in cities like New York and San Francisco with highly educated populations and high levels of local government expenditures.
The positive message is that the gap between rich and poor is not “inevitable”.
Eliminating fatal forms of cancer would also increase the average lifespan by more than 3 years, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments
Bookmark popover
Removed from bookmarks