In Toyota City, recalls are blamed on foreign components
Toyota City, about 200 miles east of Tokyo, once appeared on the map – if it appeared at all – as Koromo. But in 1959 town leaders renamed it after the up-and-coming local car producer, and twinned their modest town with the then global centre of auto production, Detroit.
The move must have seemed comically ambitious at the time, but half a century and over 170 million vehicles later, nobody is laughing at the world’s biggest automobile manufacturer. Toyota City is today far larger and incomparably richer; like Toyota’s cars it is a neat, efficient, slightly featureless place in contrast to the once all-conquering Detroit, which has become a byword for urban decline.
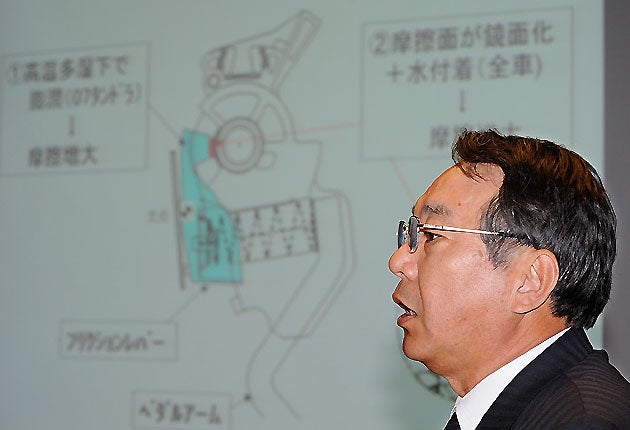
But success has come at a cost, as the firm’s problems this week show. Toyota has long been known both for the ruthless efficiency of its production line, and the matchless quality of the cars that emerged at the other end. But now the car-making behemoth has been humbled by a series of huge foreign recalls, which a shaken executive vice-president, Shinichi Sasaki admitted may cost up to $2bn (£1.25bn) in lost output and sales. The latest recall, to fix a fault that could jam accelerator pedals, involves 4.2 million cars worldwide, including roughly 180,000 in Britain.
That comes on top of another five million vehicles sent back to workshops for repair in the US, after a separate accelerator problem reportedly led to several deaths and at least a dozen class-action lawsuits in North America. Toyota was also forced to stop stateside sales and production of eight models last week, all of which will further tarnish its reputation and deal a huge blow to this year’s balance sheet, admits Sasaki. “The sales forecast is something that we’re extremely worried about,” he said this week.
Today, claims that only Toyotas made outside Japan using foreign-made parts were affected by the crisis was dealt a blow when it emerged that there have been more than 100 complaints, in Japan as well as the US, about the brakes on its new hybrid Prius model. And yet, as industry analysts have noted, the company has yet to make a formal apology for these shortcomings, let alone unveil a convincing programme for addressing them.
Experts are pondering how a company that made better, more reliable cars than almost anyone else could have ended up in such a mess. At home in Japan, which has been mostly unaffected by the recalls, the media has already named the guilty party – foreign parts makers. Toyota’s enormous global expansion has forced it to rely on local manufacturers, resulting in a drop in quality.
The faulty accelerator pedal, for example, was made by a North American company – one reason why Toyota is reportedly switching back to its decades-old domestic supplier Denso Corp. That is just one symptom of a wider problem familiar to many multinationals: how to protect quality at overseas factories, particularly when you are a company that employs 300,000 people around the world, selling in 150 countries. “Toyota set up so many plants, turning into an international company,” Keinosuke Ono, professor of business at Chubu University in Kasugai, Japan, told AP this week. “It was inevitable that rank-and-file quality is becoming endangered.”
Over two decades ago, the company began the foreign transplant of what became known as the “Toyota Way”, a system of lean production aimed at eliminating waste, producing zero defects and continually improving line performance (“kaizen”) that has transformed car-making worldwide. Some commentators also credit Toyota with a more profound innovation: shifting responsibility for production from managers back to the shop floor.
Toyota workers are not penalised for spotting problems and stopping a line, they are praised, points out Yozo Hasegawa, author of Clean Car Wars: How Honda and Toyota are Winning the Battle of the Eco-Friendly Motors. In fact, Toyota factories employ teams whose sole job is to find problems and save time and money. American factories were hampered by stalling production lines, but Toyota improvised, says Hasegawa. “When a problem arose, it would undergo repeated questioning until its roots could be traced, and a kaizen or improvement measure put in place to prevent a repeat.”
Experts say grafting that system on to overseas factories has mostly worked, but replicating Toyota’s network of trusted parts supplies, built over decades in Japan, has been more difficult. Figuring out how to fix that problem will keep the company’s top executives busy in the months to come. Meanwhile, they are praying that their mounting troubles don’t persuade buyers to switch brands. One US consumer group blames the accelerator pedal problem on at least 18 deaths in the last decade.
Only time will tell if the recalls are but potholes on Toyota’s road to world domination or signs of a deeper structural malaise, but don’t feel sorry for Toyota City yet. Although analysts expect Toyota’s market share in Europe and the US to drop to its lowest level since 2006, this is a company with deep pockets. Before its problems began last year, the car-maker had a war chest of over €19bn, helping it earn the nickname “Toyota Bank”. Toyota didn’t end General Motors’ 76-year reign as the world’s sixth-largest auto-maker by being bad at what it does. A comeback seems inevitable.
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments
Bookmark popover
Removed from bookmarks