The Big Question: Will Iraq disintegrate if the United States withdraws its troops?
Why are we asking this now?
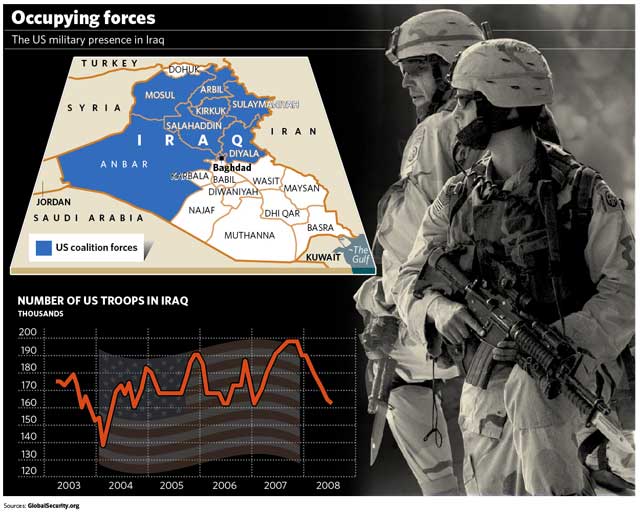
The United States and Iraq are close to agreeing a security accord under which the US would pull its combat troops out of Iraqi cities, towns and villages on 30 June 2009, and out of Iraq by 31 December 2011. This will only happen if a joint Iraqi-American ministerial committee agrees that security in Iraq has improved to the point where the half million strong Iraqi security forces can take over. Other aspects of the draft agreement show that the government of the Iraqi Prime Minister, Nouri al-Maliki, is increasingly confident of its own military and political strength.
The new accord is very different from the one the US proposed as recently as March, which would simply have continued the US occupation, much as it has been under the UN mandate, which runs out at the end of the year. The main point about the agreement, if it is implemented as expected, is that the US will cease to be the predominant military power in Iraq from next summer for the first time since the US-led coalition overthrew Saddam Hussein in 2003.
Will Iraq be able to hold together as US troops depart?
Yes it will, but not because the three main Iraqi communities love each other. The Shias are coming out the winners, and this was always inevitable once the US had decided to overthrow the predominantly Sunni regime of Saddam Hussein. Shias make up 60 per cent of the Iraqi population, and the Sunni Arabs and the Kurds are each about 20 per cent. Mr Maliki leads a Shia-Kurdish government in which the most powerful element is the Shia religious parties.
The insurgency in which 4,300 American soldiers were killed and 30,000 were wounded was a rebellion of the Sunni community. This was the war to which the world paid most attention. But there was a second savage civil war between the Sunnis and Shias, which the Shias won decisively. They now control most of the government and the army. They hold at least three-quarters of Baghdad after fierce fighting in the capital in 2005-07. The Sunnis are now too weak to set up a separate canton. The Kurds need to remain part of Iraq, however much they may yearn for independence, because otherwise they face invasion by Turkey. The central government is becoming increasingly assertive against the Kurds, particularly over the issue of who holds Kirkuk and the right to award contracts for oil exploration and exploitation.
Does this mean that the Surge worked and the US has won in Iraq?
This is mostly propaganda. The Surge was the increase in US troop levels by 30,000 men, from February 2007, and more aggressive tactics by the US army under the command of General David Petraeus.
But even before the Surge, it was clear that the Sunni community was being driven out of large parts of Iraq, above all from greater Baghdad.
There was also a backlash against al-Qa'ida, which had overplayed its hand by declaring "the Islamic State of Iraq" in late 2006. It has sought to marginalise or kill hostile Sunni tribal leaders. It killed or mutilated anybody who failed to obey its extreme fundamentalist Islamic beliefs. Hairdressers were shot dead for giving "un-Islamic" haircuts.
But, above all, the Sunnis could see that al-Qa'ida's brutal and bloody use of enormous vehicle bombs against Shias had provoked a devastating reaction. Sunni nationalist insurgents had no choice but to end their guerrilla war against the US forces and seek US support and aid. There are now 103,000 members of Al-Sahwa, or the Awakening Movement, who are paid for by the US. American military fatalities are down to only 18 so far this month.
But the fall in violence is only partly to do with the actions of the US. It is a great mistake to imagine that the US makes all the political weather in Iraq.
The main reason for the end of the Sunni insurgency against the US forces is the defeat of Sunnis by Shias in the battle for Baghdad.
Is al-Qa'ida finished in Iraq?
It is much weaker than it was. It has lost its old bastions in Anbar province to the west and in much of Baghdad. But it is a mistake to think that it is wholly eliminated. The grim evidence for this is carefully planned assassinations of Awakening Movement members, usually by suicide bombers, that would require good intelligence and organisation. Al-Qa'ida clearly still has the capacity of launching massive suicide bombs against Shia civilian targets. Crowded street markets are very difficult to protect.
Surely life in Baghdad and the rest of Iraq is getting better?
It certainly is improving, but there is a misconception outside Iraq about what this means. At the height of the Sunni-Shia sectarian conflict, some 3,000 people were being murdered every month. In July, this figure was down to about 900, according to the Iraqi Interior Ministry.
This is better, but scarcely represents a return to normal life. Baghdad is still the most dangerous city in the world. Sunnis and Shias seldom visit each other's districts.
The best barometer for the real state of security in Iraq is the ability of the 4.7 million refugees inside and outside the country to return home. There are about one in six Iraqis who have lost the places in which they used to live. Often these displaced people live in miserable conditions in Jordan, Syria or other parts of Iraq, but it is still too dangerous, despite all the talk of conditions improving in Iraq, for them to reclaim their homes.
Where does Iran stand in all this?
This is the most misunderstood element in the Iraq crisis. The present Iraqi government had two main allies: the US and Iran. Their dispute is over who should have influence over that government. Iran has played a crucial role in the success of the so-called Surge. The Iraqi army fought poorly against the militiamen of the Mahdi Army in March and April. It was Iran that mediated a ceasefire on the Baghdad government's terms. It was Iran which pressured the Mahdi Army's leader, Muqtada al-Sadr, to call his man off the streets. A prime reason why Iraq is not going to disintegrate is that Iran does not want it to.
So the departure of US troops from Iraq will not mean a renewed civil war?
No. The main civil war is over. The Shias won and the Sunnis lost. But the Sunni minority in Baghdad looks vulnerable without American protection. The Iraqi army is increasingly moving against the Sunni Awakening Movement in Anbar province and elsewhere.
Will Iraq fall apart if the Americans go?
Yes...
* Shias, Sunnis and Kurds seem unable to agree on anything
* Almost five million Iraqis are refugees and cannot return to their homes
* The Americans are the only non-sectarian military force
No...
* The Shia-Kurdish government looks as if it is here to stay
* Sectarian killings are down, though Shias, Sunnis and Kurds live in their own enclaves
* The occupation has always been opposed by the majority of Iraqis outside Kurdistan
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments
Bookmark popover
Removed from bookmarks