Glow-in-the-dark tampons could help identify water pollution in Britain's rivers
Even small amounts of sewage could be picked up by tampons suspended in contaminated water
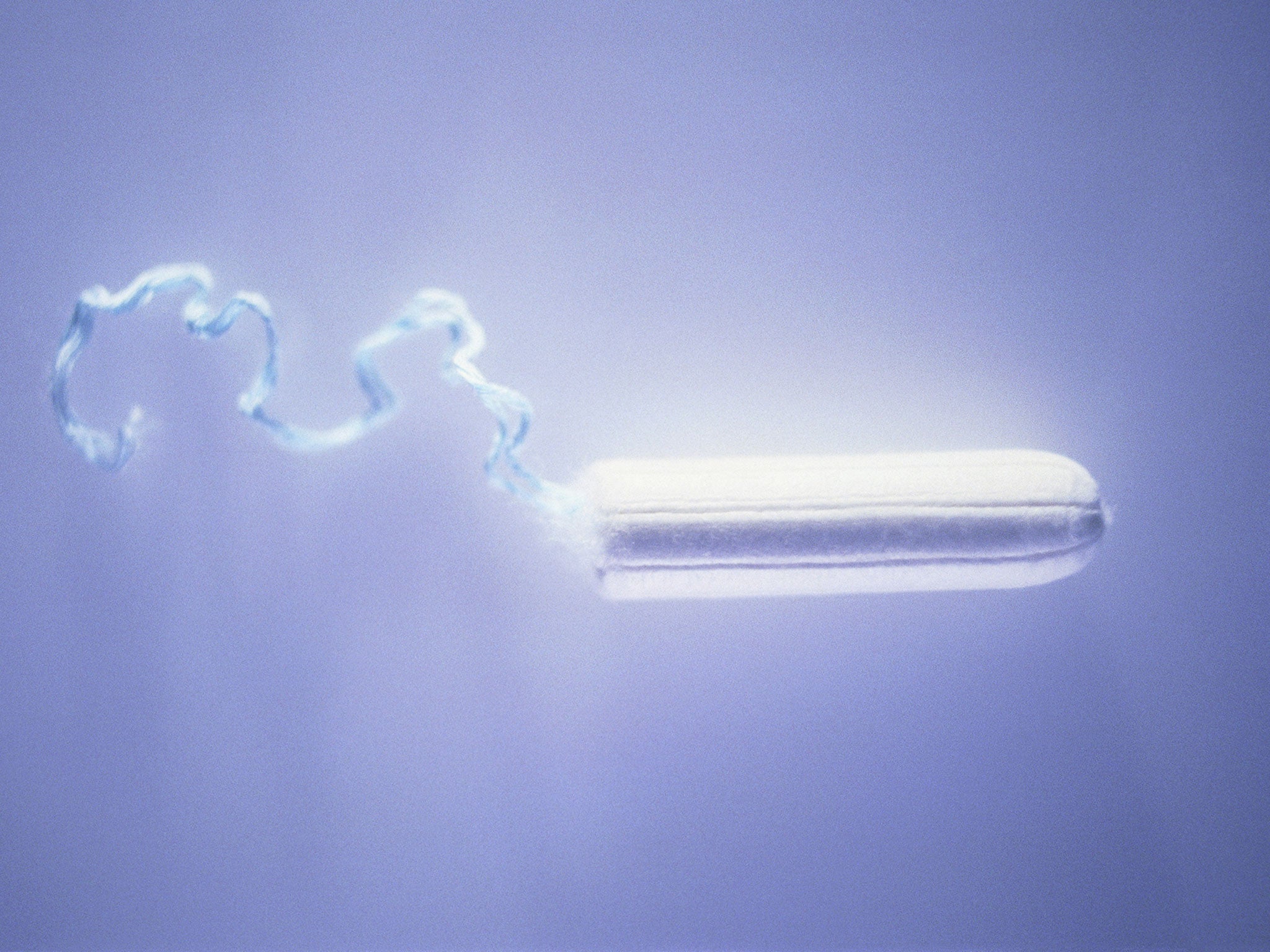
Tampons could be a cheap and effective way to identify sewage seeping into rivers and streams in Britain, scientists have suggested.
A team at the University of Sheffield found that the natural, untreated cotton found explicitly in tampons is able to absorb chemicals commonly used in toilet paper, laundry detergent and shampoo – used to enhance whites and brighten colours – which show up under ultra violet light.
Published in the Water and Environment Journal, the findings show that even small amounts of sewage could be picked up by tampons suspended in contaminated water and glow under UV light.
Professor David Lerner, who led the study, said: "More than a million homes have their waste water incorrectly connected into the surface water network, which means their sewage is being discharged into a river, rather than going to a treatment plant.
"It’s very difficult to detect where this is happening, as the discharge is intermittent, can’t always be seen with the naked eye and existing tests are complex and expensive.
"The main difficulty with detecting sewage pollution by searching for optical brighteners is finding cotton that does not already contain these chemicals. That’s why tampons, being explicitly untreated, provide such a neat solution. Our new method may be unconventional – but it’s cheap and it works."
Lerner hopes to trial the method at a larger scale to identify all the sources of sewage pollution on the Bradford Beck, the river which runs through the city of Bradford.
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments
Bookmark popover
Removed from bookmarks