Scientists discover gigantic ‘shark-toothed’ dinosaur that dominated food chain before tyrannosaurs
Scientists say the dinosaur may have been twice the length, and over five times heavier than a tyrannosaur
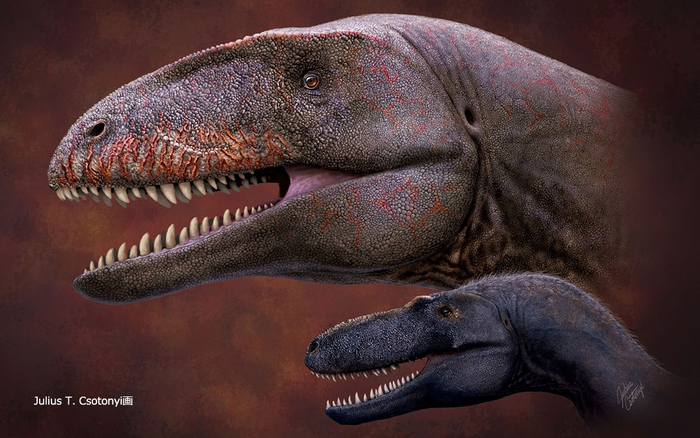
Scientists have discovered a new gigantic dinosaur with shark-like teeth that lived 90 million years ago and was an apex predator of its time, ruling the food chain on land before the advent of the Tyrannosaurus rex.
A fossil jawbone of the beast, now named Ulughbegsaurus uzbekistanensis, was unearthed in Uzbekistan, representing the first record of an apex predator dinosaur of this era from Central Asia.
According to the researchers, including Kohei Tanaka from the State Geological Museum of the State Committee of the Republic of Uzbekistan, the 8-metre-long dinosaur weighed more than a tonne.
Based on estimations from the analysis of the fossil remains, the scientists say U. uzbekistanensis may have been twice the length and over five times heavier than a tyrannosaur.
The jawbone fossil analysed in the study was initially found in Uzbekistan’s Kyzylkum Desert in the 1980s, and rediscovered by scientists in 2019 in a museum collection.
“Among theropod dinosaurs, the size of the maxilla (upper jawbone) can be used to estimate the animal’s size because it correlates with femur length, a well-established indicator of body size,” Tanak said in a statement.
“Thus, we were able to estimate that Ulughbegsaurus uzbekistanensis had a mass of over 1,000 kg, and was approximately 7.5 to 8.0 meters in length, greater than the length of a full-grown African elephant,” he added.
The study, published in the journal Royal Society Open Science, noted that U. uzbekistanensis belongs to a group of “shark-toothed dinosaurs” called carcharodontosaur.
“The discovery of Ulughbegsaurus records the geologically latest stratigraphic co-occurrence of carcharodontosaurid and tyrannosauroid dinosaurs from Laurasia, and evidence indicates carcharodontosaurians remained the dominant predators relative to tyrannosauroids, at least in Asia,” the scientists noted in the study.
The scientists say dinosaurs in the carcharodontosaur group were usually larger than tyrannosaurs, sometimes reaching weights greater than 6 tonnes.
The carcharodontosaurs likely disappeared some time around 90 million to 80 million years ago, providing more opportunities for tyrannosaurs to dominate the ecosystem, grow in size, and take over as apex predators.
“Thus, its discovery fills a geographic gap in the clade between Europe and East Asia and shows that carcharodontosaurians were widespread across Asia,” the researchers wrote in the study.
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments
Bookmark popover
Removed from bookmarks